Unraveling the Mystery of the Varicella Zoster Virus
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a painful and often debilitating viral infection caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox. While shingles primarily affects older adults and individuals with weakened immune systems, it can occur at any age, posing significant challenges to those affected and underscoring the importance of understanding this complex condition.
Related searches
-
What Does Shingles Look Like

-
Pictures Of Shingles

-
Early Shingles

-
Are Shingles Contagious

-
How To Cure Shingles In 3 Days

-
Is Shingles Contagious

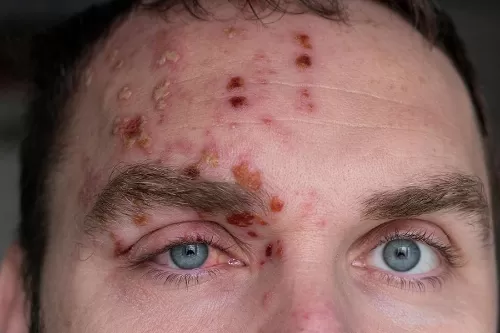
Shingles: The Viral Resurgence
The varicella-zoster virus lies dormant in nerve cells after causing chickenpox, but can reactivate years later, leading to the development of shingles. The exact triggers for reactivation remain unclear, but factors such as aging, stress, and compromised immune function are believed to play a role. When the virus reactivates, it travels along nerve pathways to the skin, resulting in the characteristic rash and painful blisters associated with shingles.
Navigating the Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs of Shingles
Shingles typically begins with a tingling or burning sensation in a specific area of the body, followed by the appearance of a red, painful rash. The rash progresses into fluid-filled blisters that eventually crust over and heal within a few weeks. In addition to the rash, individuals with shingles may experience symptoms such as fever, headache, and fatigue. The pain associated with shingles can be severe and persistent, often requiring medical intervention to manage effectively.
Complications and Consequences: Understanding the Impact of Shingles
While shingles is usually a self-limiting condition, it can lead to complications that warrant medical attention. One of the most common complications is postherpetic neuralgia, a condition characterized by persistent nerve pain in the affected area long after the rash has healed. Other potential complications include bacterial skin infections, vision loss if shingles affects the eyes, and neurological problems if the virus spreads to the brain or spinal cord. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to minimize the risk of complications and alleviate symptoms.
Prevention and Protection: The Role of Vaccination
Vaccination against shingles is the most effective way to reduce the risk of developing the infection and its associated complications. The shingles vaccine, also known as the herpes zoster vaccine, is recommended for adults aged 50 and older, as well as certain high-risk populations, such as individuals with weakened immune systems. By stimulating the body's immune response to the varicella-zoster virus, the vaccine helps prevent reactivation and reduce the severity of shingles symptoms in those who do contract the virus.
Empowering Through Awareness and Action
In conclusion, shingles represents a significant public health concern with far-reaching implications for individuals and communities worldwide. By deepening our understanding of the varicella-zoster virus and its reactivation, promoting early recognition of shingles symptoms, and advocating for vaccination as a preventive measure, we can mitigate the impact of this debilitating infection and improve the quality of life for those affected. Through education, awareness, and proactive healthcare interventions, we can work together to combat shingles and pave the way for a healthier, more resilient future.
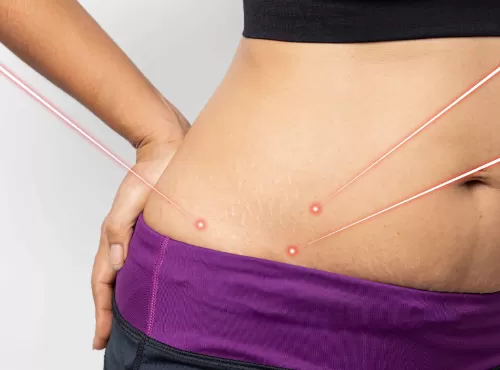
Laser Fat Removal: A Modern Solution to Stubborn Fat
In today’s world, many people seek safe and effective methods to remove stubborn fat and achieve a toned appearance without undergoing invasive surgery. One of the most innovative and non-invasive options available is laser fat removal. This technology uses laser energy to target and break down fat cells in specific areas of the body. Here’s an overview of how laser fat removal works, its benefits, and considerations for those interested in this cutting-edge treatment. Laser fat removal is a non-surgical procedure that uses focused laser energy to target and eliminate localized fat deposits. The procedure is also known by various brand names, including CoolSculpting and SculpSure, which are some of the most popular technologies used in laser fat reduction.
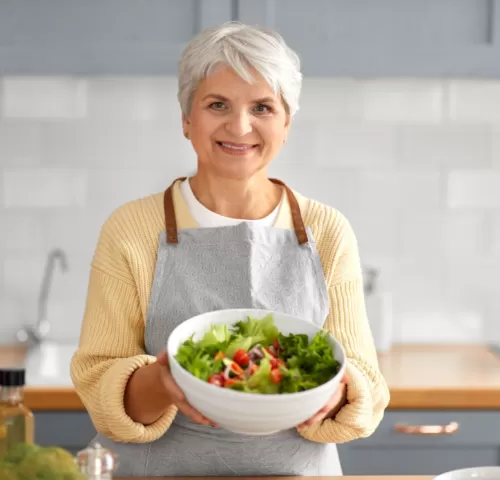

Seniors and Low Carb Diets: Benefits and Risks
In recent years, the low carbohydrate diet plan has gained popularity among seniors seeking to manage weight, improve energy, and enhance overall health.

Pharmaceutical Equipment: Essential Machines for Modern Drug Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical equipment refers to specialized machinery used in drug manufacturing, packaging, and quality control. These machines play a crucial role in ensuring the production of safe, high-quality medicines while meeting strict regulatory standards.

How to Get Rid of Lower Belly Fat: Effective Tips and Strategies
Lower belly fat is a common concern for many people, especially women. This stubborn area can be challenging to target, but with the right approach, it is possible to achieve a flatter, toned abdomen. Let’s explore the best strategies to lose lower belly fat and regain confidence.

Prepared Foods: The Ultimate Solution for Healthy and Convenient Living
Prepared foods have revolutionized the way we approach daily meals, offering a seamless blend of health, convenience, and flavor. With busy lifestyles becoming the norm, turning to prepared meal delivery services ensures you can enjoy nutritious meals without the hassle of cooking or meal planning. These services have gained immense popularity, and it’s no surprise they are now recognized as a cornerstone of modern dining solutions.

Finding the Right Rehab Centers: Your Path to Recovery
When you or a loved one is struggling with addiction or substance abuse, finding the right rehab facility is essential. Understanding the different types of rehabilitation options available can help you make informed decisions for effective recovery. Below, we explore various aspects of rehab centers and what to consider when choosing the right one for you.
 By:
ADA
By:
ADA