Robots with Empathy: Can Machines Really Understand Feelings
The concept of a robot sensing or responding to human emotions is no longer confined to sci-fi movies. Today, machines equipped with advanced sensors and algorithms can recognize facial expressions, vocal tones, and even physiological signals like heart rate. But does this mean robots truly "understand" emotions, or are they simply following programmed instructions? The answer reveals both the potential and the limits of artificial empathy—and why it matters for how we interact with technology.
Related searches

How Robots Detect Emotions
Robots lack consciousness, but they can be trained to identify emotional cues. Cameras analyze facial movements—a furrowed brow might be labeled "frustration," while a smile could signal "happiness." Microphones detect changes in speech patterns, like a trembling voice indicating sadness. Some robots even integrate wearable devices to track physical responses, such as sweating or increased pulse. These systems rely on vast datasets of human behavior, teaching robots to match inputs with predefined emotional categories. However, this process is purely mechanical: a robot doesn't "feel" sadness when it detects tears; it simply triggers a prewritten response, like offering a tissue or soothing words.
Why Emotional Robots Are Being Developed
The goal isn’t to create machines that experience emotions but to make technology more adaptive. In healthcare, robots with emotion-detection skills can adjust their interactions with patients—speaking softly to someone in distress or encouraging medication adherence. In education, tutoring robots might slow down explanations if a student seems confused. Customer service bots use sentiment analysis to escalate frustrated users to human agents. By mimicking empathy, robots aim to bridge gaps in industries where human resources are stretched thin. Yet this raises ethical questions: Can a machine’s scripted kindness ever replace genuine human care?
The Risks of Confusing Code with Compassion
While robots can simulate empathy, they cannot reciprocate it. A machine might "comfort" a grieving person by reciting condolences from a script, but it has no capacity to share sorrow or offer personal wisdom. This illusion of understanding could lead to overreliance on robots for emotional support, especially in vulnerable populations like isolated seniors or children. Critics warn that mistaking algorithmic responses for real empathy might erode human connections, making synthetic interactions a Band-Aid for societal loneliness.
The Line Between Tool and Companion
Robots are tools, not companions. Their value lies in consistency and efficiency, not emotional depth. For example, a therapy robot might remind someone to take medication or practice breathing exercises—tasks that require reliability, not genuine empathy. However, developers must avoid designs that anthropomorphize robots excessively, as this could mislead users into believing machines possess human-like intentions or feelings.
Conclusion
Robots may mimic empathy through sensors and scripts, but they remain sophisticated tools—not sentient beings. While their ability to detect emotions can enhance healthcare, education, and customer service, these machines lack the lived experience and reciprocal understanding that define genuine human connection. The real promise of "empathetic" robots lies not in replacing compassion, but in supporting it—freeing humans to focus on the irreplaceable warmth of personal care. As we integrate these technologies, we must safeguard a truth no algorithm can replicate: empathy's power stems not from flawless execution, but from the messy, heartfelt humanity that machines will never possess.

Powering Your Home with Sunshine: How Clean Energy is Slashing Electric Bills Nationwide
In 2025, clean energy is no longer a niche trend—it’s a mainstream solution transforming how families power their homes. Solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems are cutting electric bills while reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This guide explores how clean energy technologies are making homes more affordable, sustainable, and resilient—all while combating climate change.

The Molecular Detective: How Mass Spectrometry Uncovers Hidden Health Clues in Your Breath
A single breath holds more than just air—it carries invisible clues about your health. In 2025, scientists are harnessing mass spectrometry to decode these molecular signals, offering a non-invasive way to detect diseases like cancer, diabetes, and infections. This technology acts as a “molecular detective,” analyzing breath samples to reveal hidden health risks—all without needles or extensive medical procedures.

Learning in AI: The Ultimate Guide to AI Machine Learning Training in 2025
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming industries at an unprecedented pace. From AI predictive analytics to machine learning in manufacturing, AI-powered technologies are driving innovation, efficiency, and automation. Whether you're looking to learn artificial intelligence online, enroll in AI and ML training, or explore the vast potential of big data, AI, and machine learning, now is the time to dive in.

Start Your Journey in Digital Marketing: Careers, Opportunities, and Growth
The digital marketing industry is booming, offering a wide range of career paths and exciting opportunities. If you're considering a career in digital marketing or want to boost your online presence, this guide covers various aspects of the field, from freelance digital marketing to working with specialized recruitment agencies.
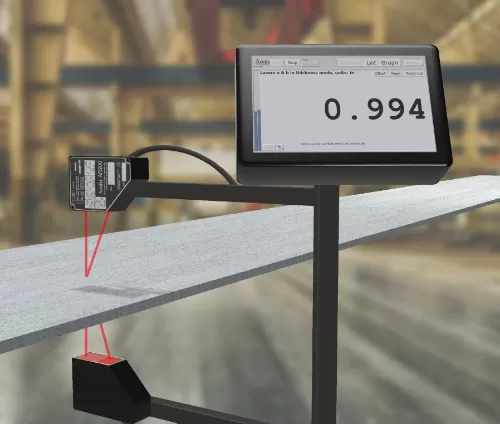
The Ultimate Guide to Measurement Sensors: Precision, Efficiency, and Innovation
Measurement sensors are revolutionizing industries by providing accurate data for automation, quality control, and safety monitoring. From manufacturing to healthcare and automotive applications, measurement sensors are essential for improving efficiency and performance.

Solar Panels: Harnessing the Power of the Sun for Sustainable Energy
Solar panels are a key technology in the transition to renewable energy, converting sunlight into electricity to power homes, businesses, and even vehicles.
 By:
Lorna
By:
Lorna