Understanding Heart Disease: A Growing Concern for Middle Aged Americans
Heart disease remains one of the leading health concerns for middle-aged Americans, affecting millions and continuing to be a significant cause of mortality. As awareness of this condition increases, it is crucial to understand its risk factors, symptoms, and prevention strategies, especially in light of recent health trends and research.
Related searches
-
Heart Valve Blockage Treatment

-
Heart Valve Specialist

-
Hocm Medical

-
Obesity And Heart Disease

-
Cardiovascular Hospital

-
Adult Congenital Heart Disease
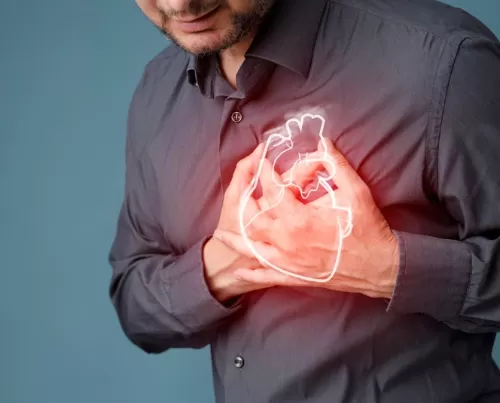


The Current Landscape
Recent studies show that heart disease is increasingly prevalent among adults aged 45 and older. Factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and unhealthy diets contribute significantly to this trend. The COVID-19 pandemic further underscored the importance of cardiovascular health, as those with existing heart conditions faced higher risks of severe illness.
Common Risk Factors
High Blood Pressure: Often called the "silent killer," hypertension can lead to heart disease if left unmanaged. Regular check-ups and monitoring are vital.
High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Diabetes: Diabetes significantly raises the risk of heart disease. Managing blood sugar levels through diet and medication is essential.
Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, poor diet, and lack of physical activity are major contributors to heart disease. Making healthier choices can dramatically reduce risk.
Symptoms to Watch For
Understanding the warning signs of heart disease is crucial for early intervention:
Chest Pain or Discomfort: Often described as pressure, squeezing, or fullness, this can be a sign of a heart attack.
Shortness of Breath: This can occur during rest or physical activity and may indicate underlying heart issues.
Fatigue: Unusual tiredness, especially in women, can be a significant warning sign.
Palpitations: Irregular heartbeats or a racing heart can indicate an underlying problem.
Prevention Strategies
Fortunately, there are many ways to reduce the risk of heart disease:
Healthy Eating: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support heart health. The Mediterranean diet, in particular, has been linked to lower heart disease rates.
Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week. Exercise can help lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and maintain a healthy weight.
Quit Smoking: If you smoke, seek resources to help you quit. Smoking cessation significantly reduces the risk of heart disease.
Regular Check-ups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider for blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes screenings are crucial for early detection and management.
Conclusion
Heart disease is a pressing concern for middle-aged Americans, but with awareness and proactive measures, it can often be prevented or managed. By understanding risk factors, recognizing symptoms, and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, individuals can take control of their cardiovascular health. As we continue to prioritize health in our daily lives, let’s focus on building a foundation for a healthier future.

Finding the Right Rehab Centers: Your Path to Recovery
When you or a loved one is struggling with addiction or substance abuse, finding the right rehab facility is essential. Understanding the different types of rehabilitation options available can help you make informed decisions for effective recovery. Below, we explore various aspects of rehab centers and what to consider when choosing the right one for you.

Advancements in Medical Programs: A Glimpse into 2025
As we progress through 2025, the medical education landscape is undergoing significant transformations worldwide. Institutions and governments are implementing innovative programs and policies to address healthcare challenges and enhance medical training. Here are some notable developments:

Boost Your Performance Exploring Male Enhancement Gummies
Male enhancement gummies are dietary supplements designed to improve sexual performance and stamina, offering a convenient and discreet option.

Exploring the Benefits of Telemedicine and Telehealth Services
With the rapid advancement of technology, healthcare is transforming. Telemedicine and telehealth services are becoming more popular, offering convenient, efficient, and accessible medical care. This article explores the benefits of telehealth options, covering services such as urgent care, mental health support, and insurance partnerships to help readers understand the value of these innovative healthcare solutions.

Maximizing Returns: Navigating the Landscape of CD Rates
Certificate of Deposit (CD) rates serve as a cornerstone of conservative investment strategies, offering individuals a reliable means of preserving and growing their savings over time. As financial markets fluctuate and economic conditions evolve, understanding CD rates becomes essential for investors seeking to optimize their returns while mitigating risk. From assessing current market trends to exploring strategies for maximizing yields, navigating the landscape of CD rates requires careful consideration and informed decision-making.
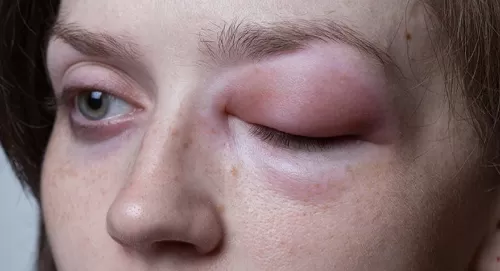
Effective Management and Treatment of Hereditary Angioedema (HAE)
Hereditary Angioedema (HAE) is a rare genetic disorder that causes episodes of severe swelling, typically in the hands, feet, face, and airway. Managing HAE effectively requires a comprehensive approach, from accurate diagnosis to ongoing treatment. In this guide, we will explore the best ways to manage and treat hereditary angioedema, including advanced therapies, top-rated treatment centers, and expert specialists.
 By:
Maric
By:
Maric